CALL TO ACTION ~
CALL TO ACTION ~
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
PWS is a rare genetic disorder that affects a child's appetite, growth, metabolism, cognitive functioning, and behavior. Continuous feelings of insatiable hunger (hyperphagia) and slowed metabolism are present. PWS symptoms and behaviors exist on a spectrum. Therefore, children will exhibit different degrees of common PWS traits, which can also change as the child gets older.
PWS educational Resources
Prader-Willi Syndrome: A Primer for School Psychologists
Bedard, K.E., Pacha, D., Griffith, A.K., & Ward, S. (2024). Prader-Willi Syndrome: A primer for school psychologists. Children and Youth Services Review.
IEP Guides & references
Alphabet Soup of Special Education (acronyms)
Transitioning from an IFSP to an IEP
IEP Supports: Accommodations & Modifications
Medical vs Educational Evaluations
Education & Learning
PWS Awareness—Fact Sheet
Educational Implications of PWS
7 Common PWS Learning Difficulties
Updated PWS Overview for School Personnel (trifold)
Behavior & Emotional Regulation
6 Key Behavioral Features of PWS
Most Common Outburst Triggers In PWS
C.L.E.A.R. Strategies to Empower Empathy
Strategies to Support Self-Regulations at School
Schedule Change Cards & Implementation
Effective Adult Response Strategies
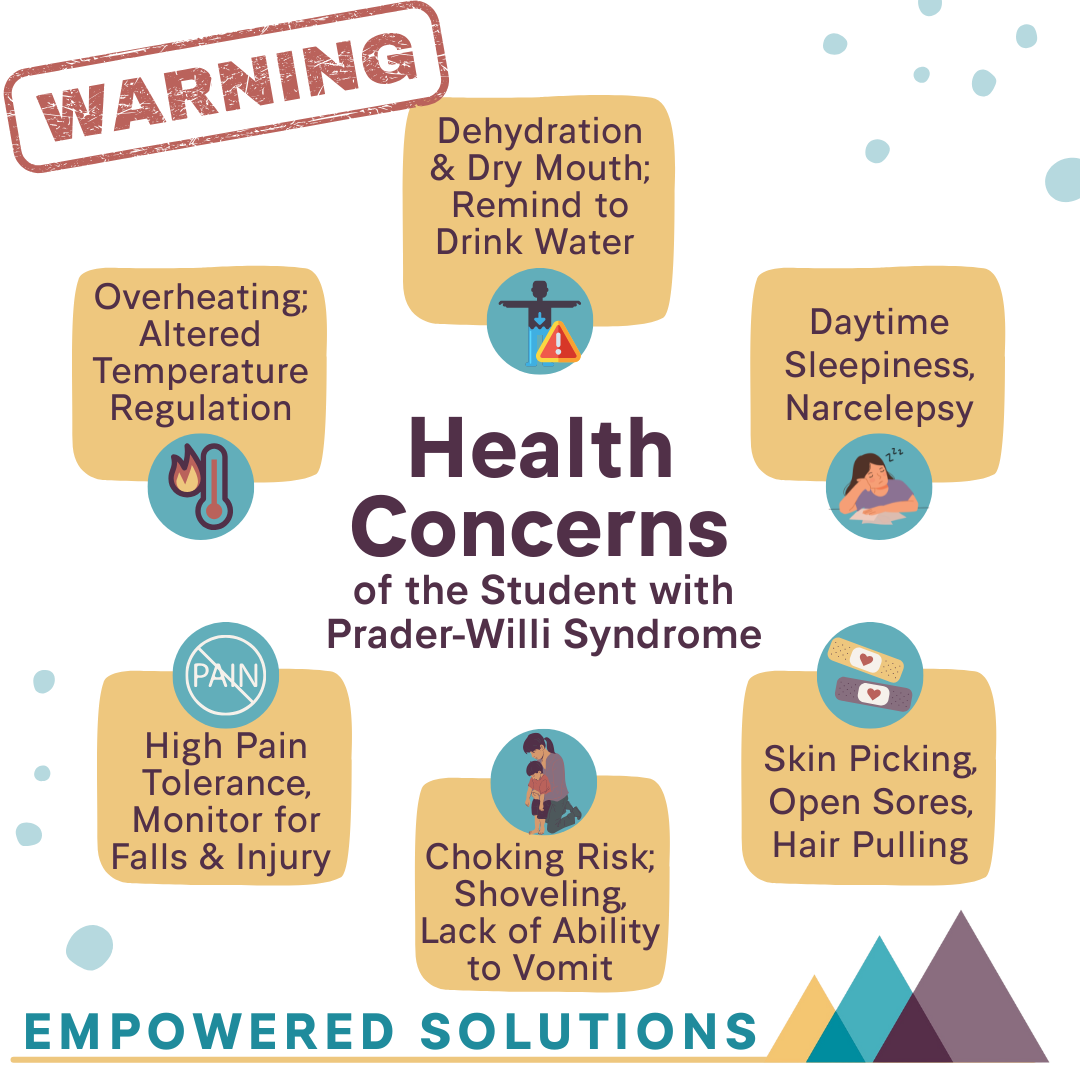
Health & Nutrition at School
Health Concerns & Strategies at School
Parents’ Guide to Individualized Health Plans (IHP)
Nutrition and Healthy Eating
Nutritional Phases in Prader-Willi Syndrome
Ensuring Food Security in the Classroom
Questions to Evaluate Food Security at School
Request your Free copies of these PWS School Resources today!
“Children with PWS can no more control their appetite than they can control a sneeze. It is imperative that the child’s environment be modified; trying to change a child’s desire for food or food-seeking behavior is futile without limiting access.”
For additiONAL INFORMATIOn visit these leading PWS Organizations
Special Education Online Resources
If you or someone you know is struggling,
free and confidential resources are available 24/7:
For immediate, life-threatening emergencies, call 911.
For mental health crises, you can call or text 988.
For non-emergency support and local resources, you can call or text 211.